Window Panes
ABC of Window Panes.

Double-glaze Windows
One of the main elements of any aluminum window is glass. Depending on the size, structure and division into quarters, the glass area may constitute from 25% to 95% of its total area. Depending on the individual needs of customers, modern windows can be glazed not only with single glazing, but also two or even three-chamber double glazing with strictly defined and tested properties.
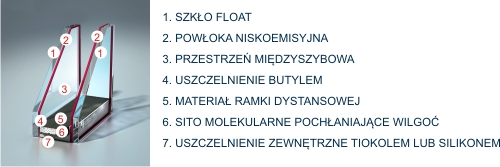
Information
Stosowane szyby w A.M.C. STYLE:
- low-emmisioned,
- sound-absorbing,
- sungalsses
- safe,
- anti-burglary,
- reflective and mirrored,
- reflective convex,
- absorbtive,
- bevelled in different widths of the rim,
- sandblasted,
- stained glass,
- ornamental,
- colored in mass,
- chemically etched,
- heat-resistant,
- reinforced.
Mirrors - any shape, size, thickness and type of bevelling
Fittings are used depending on the model and type of windows as well as their purpose:
EURO WINDOWS - Winkhaus multi-point locking fittings - one of the best companies in the European market. Reliable, strong, with a number of additional options increasing the comfort and safety of window use, e.g. with a multi-stage window tilt mechanism and multiple anti-burglary protection.
Hardware used for windows and doors: WINKHAUS, Fapim and Savio.
DOUBLE-GLAZED WINDOWS PARAMETERS
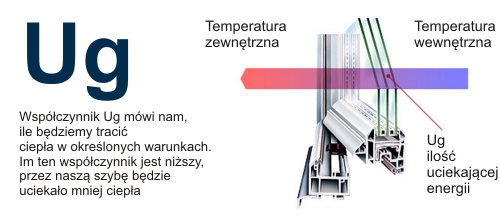
"Ug" Heat Transfer Coefficient
This factor can be described as the amount of heat lost per square meter of glass under steady conditions, when the difference between the outside and inside is 1 * K (or 1o C).
The lower the value of the "Ug" heat transfer coefficient of the glass, the better the glass protects against heat loss. The unit of the heat transfer coefficient is W / (m2 * K).
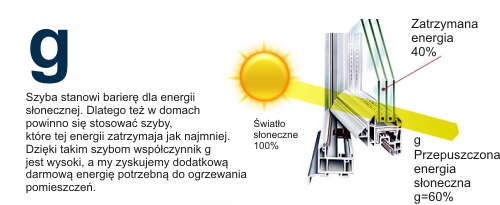
"g" Heat Transfer Coefficient
Solar energy transmission is a parameter that shows how much of the solar radiation falling at an angle close to 90 ° is transmitted through the glazing into the room. Total energy transmission coefficient "g" is always given as percent value or a decimal. The higher the percent or decimal value of the total energy transmission coefficient "g", the greater the passive gains of energy goesthrough the glass into the room.
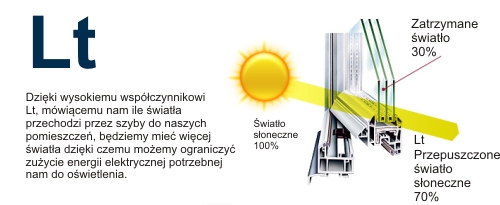
"Lt" Heat Transfer Coefficient
The light transmission coefficient is a parameter that shows how much of the visible light falling at an angle close to 90 ° is transmitted through the glass. The "Lt" light transmission coefficient is always given as percent value. The higher percent value of the light transmission coefficient, the more light goes through the glass into the room.
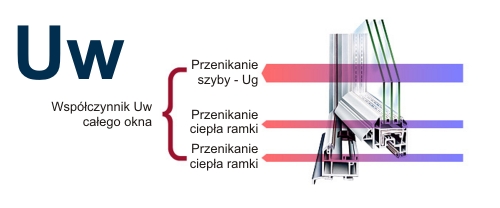
"Uw" Heat Transfer Coefficient
This factor can be described as the amount of heat lost by a structural element, e.g. a window under certain conditions when the difference between the outside and inside is 1 * K (or 1o C).
The lower the value of the "U" heat transfer coefficient of the glass, the better the window protects against heat loss. The unit of the heat transfer coefficient is W / (m2 * K).
The "U" Coefficient is influenced by such elements as:
- * heat transfer coefficient of the glass "Ug"
- * spacer frame
- * type of window frame (aluminum, PVC, wood)
- * seals
THERMAL BRIDGE
As a result of the use of spacers, a linear thermal bridge is created. Heat passes through the metal profiles almost unhindered to the outside, around the perimeter of the entire window in the area where the glass pane and the frame join. This effect not only has a negative result on the heat balance of the building, but also leads to the cooling of the temperature of the glass surface inside the room at its edge. When the temperature of the glass surface drops below a certain temperature of so-called dew point, at this very place forms a condensation - deterioration of comfort and hygiene is often reported by users. Apart from the aspect of harm to the health of residents, the window frame may be damaged as the final result.
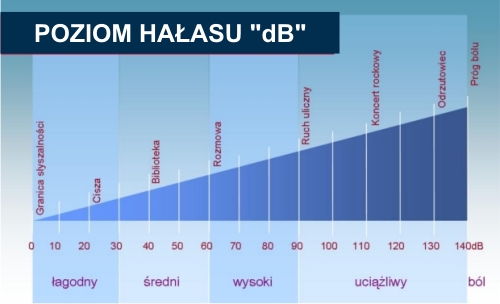
"Rw" Sound Transfer Coefficient
The acoustic insulation of a given partition is described by the R index, which expresses the difference between internal and external noise. Designers select the R sound insulation of individual structural elements to achieve the required sound insulation. The acoustic insulation of a structure is determined by an appropriate calculation method, e.g. specified in the PN-EN 12354-3 standard.
Weighted Sound Reduction - Rw
The weighted sound reduction Rw is calculated from the combination of the measured R values (16 values for 16 bands 1/3 octave, between 100 Hz and 3150 Hz) and the reference curve. The reference curve is constructed in such a way that the mean downward deviation of the curve from the measured values obtained is less than 2 dB. The value indicated by the curve determined in this way for the frequency of 500 Hz is called the weighted sound insulation Rw (dB).
Rw is a global, general indicator: the same indicator can refer to measured sound reduction curves (curves with different course).
Correction for different types of acoustic spectrum (C and Ctr)
The best result is achieved when the structure provides good sound insulation in all frequencies where the noise source is strong. So far, the acoustic insulation of a given structure has been assessed on the basis of one Rw index, without taking into account the characteristics of the noise source. This could lead to wrong investments and, consequently, to unsatisfactory noise attenuation.
To avoid this kind of situation, a uniform Rw (C; Ctr) index has been developed. The lower case "tr" is derived from the word "trafic". Correction C (dB) is used for high-frequency noise sources, e.g. high-speed traffic, high-speed rail traffic, airplanes flying nearby, sounds of everyday life, human speech, children playing. Ctr (dB) is used for low frequency noise sources, e.g. disco music, slow rail traffic, planes in the distance. Corrections are calculated from the weighted A acoustic spectra:
- C: pink noise;
- Ctr: traffic noise.
Both corrections are usually negative numbers and their application does not mean that a too favorable value of sound insulation will be corrected downwards. They are calculated by measurement laboratories and appear next to the sound reduction value Rw.
ORNAMENTAL GLASS
Ornamental glass is clear, colored or wired glass. This translucent glass is obtained by rolling liquid glass between two cylinders. One of the cylinders has an engraved pattern that is embossed on the glass during the production process.
Ornamental glass is perfect for bright interiors that provide a sense of privacy. The offer includes a wide range of patterns, colors and textures, matching the interior design of apartments and non-residential premises.
Some of the uses are:
- partitions and sliding walls;
- glass and glazed doors;
- windows;
- shower cubicles and tub covers;
- furniture (desks, tables, counters, shelves);
- barriers for indoor and outdoor use;
- small urban architecture.
BENEFITS::
Aesthetic values – Ornamental glass transmits light, subtly dispersing it, thanks to which it harmoniously harmonizes with any style of interior design, both classic and modern.
- Light and privacy – Ornamental glass separates the space, illuminating it and giving it perspective at the same time. Thanks to these properties, its use allows for:
optical enlargement of living rooms with pleasantly diffused light;
giving the interior a homely, intimate atmosphere, thanks to isolating from undesirable views from the outside.
- Easy to keep clean – Ornamental glass is easy to clean.






